|
|
本帖最后由 tomorrow 于 2010-6-4 10:26 编辑
Homology types:
共四种类型,图中红色的点代表基因复制,蓝色的点代表基因物种分化
Orthologues : any gene pairwise relation where the ancestor node is a speciation event.
We predict several descriptions of orthologues.
ortholog_one2one
ortholog_one2many
ortholog_many2many
apparent_ortholog_one2one (is a special case, see below)
Paralogues : any gene pairwise relation where the ancestor node is a duplication event.
We predict several descriptions of paralogues.
within_species_paralog
between_species_paralog
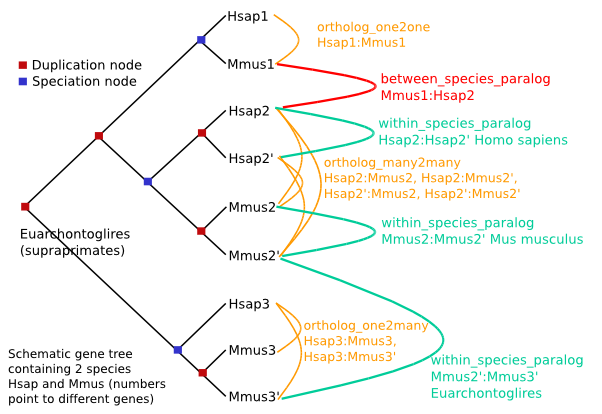
A within_species_paralog corresponds to a relation between 2 genes of the SAME species where the ancestor node has been labelled as a duplication node e.g. H2:H2', M2:M2' but does not necessarily mean that the duplication event has occurred in this species only. For example, M2':M3' are also within_species_paralog but the duplication event has occurred in the common ancestor between species H and species M. If H is human and M Mouse, the taxonomy level "times" the duplication event to the ancestor of "Euarchontoglires".
A between_species_paralog corresponds to a relation between 2 genes of DIFFERENT species where the ancestor node has been labelled as a duplication node e.g. M1:H2 or M1:H3.
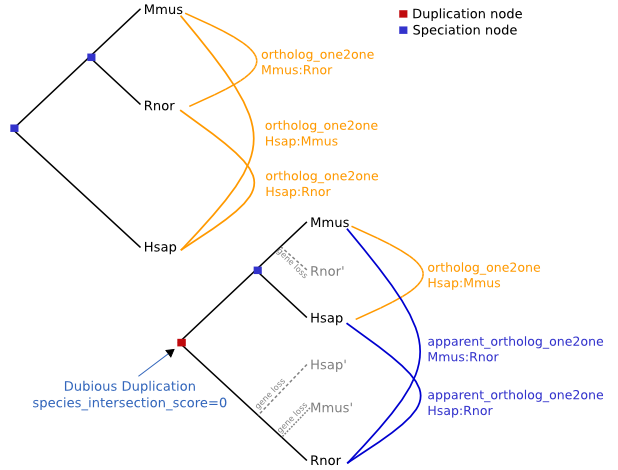
Special cases of between_species_paralog can be singled out where they can be characterised as one2one relations. Such cases are then relabelled apparent_ortholog_one2one. Apparent orthologs can be the results of real duplication followed by gene loss (as shown in the picture below), but can also be the results of a wrong gene tree topology and wrong duplication node labelling.
|
|